
If you’re using Istio or Linkerd, you’ve already solved one of the hardest parts of managing traffic in Kubernetes. But did you know you’re also 90% of the way to unlocking ephemeral environments? These lightweight, on-demand environments can transform how your team develops and tests applications — giving you faster iteration, safer deployments and better software quality.
Why Ephemeral Environments Matter
Ephemeral environments offer immense benefits. Developers get fast feedback on changes without waiting for long CI builds. QA teams can validate behavior in isolated, production-like environments, significantly reducing the risk of regressions. This approach fosters continuous improvement and deployment, helping teams move faster with high confidence in their releases.
For modern organizations, ephemeral environments are becoming essential. They enable faster iteration, improve collaboration between developers and QA, and reduce risks by catching issues earlier in the development process. Teams that adopt them can avoid many of the pitfalls associated with traditional shared staging environments.
Why Service Meshes Change the Game
The traditional approach to ephemeral environments involves duplicating the entire microservice stack in separate Kubernetes namespaces or clusters. While this provides isolation, it introduces significant challenges. Life cycle management becomes complex, costs rise as infrastructure is duplicated and spin-up times can deter thorough testing. These environments also risk becoming outdated quickly without constant updates, especially in fast-moving microservices architectures, making test results unreliable.
A more efficient approach is leveraging service mesh capabilities for tenancy-based environments. Instead of duplicating entire stacks, this approach focuses on testing changes against shared dependencies already in the Kubernetes cluster. The service mesh handles routing and traffic control, allowing multiple environments to run simultaneously without the cost and complexity of full-stack replication.
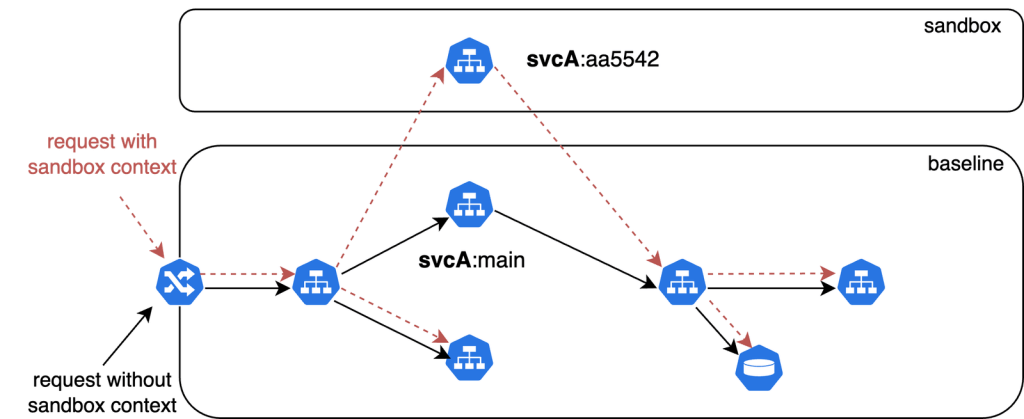
At scale, request-level tenancy segments traffic cleanly, providing isolated environments without heavy infrastructure duplication. Service meshes like Istio or Linkerd provide a lightweight, scalable solution that simplifies management and keeps operational costs low.
Real-World Examples: Scaling Ephemeral Environments
Industry leaders like Uber and DoorDash have long used scalable, on-demand environments to reduce deployment risks and boost developer efficiency. Uber’s SLATE allows isolated testing at scale, helping developers catch issues early and speed up releases. DoorDash takes a similar approach, ensuring every change is tested in isolation before going into production.
With service mesh observability and tools like OpenTelemetry, teams gain deep insights into request flows and performance across multiple environments. This makes debugging faster and prevents cross-environment interference. Developers can deploy isolated services with full routing control and avoid conflicts, making it easier to catch issues that shared staging environments often miss.
How Tenancy-Based Ephemeral Environments Work
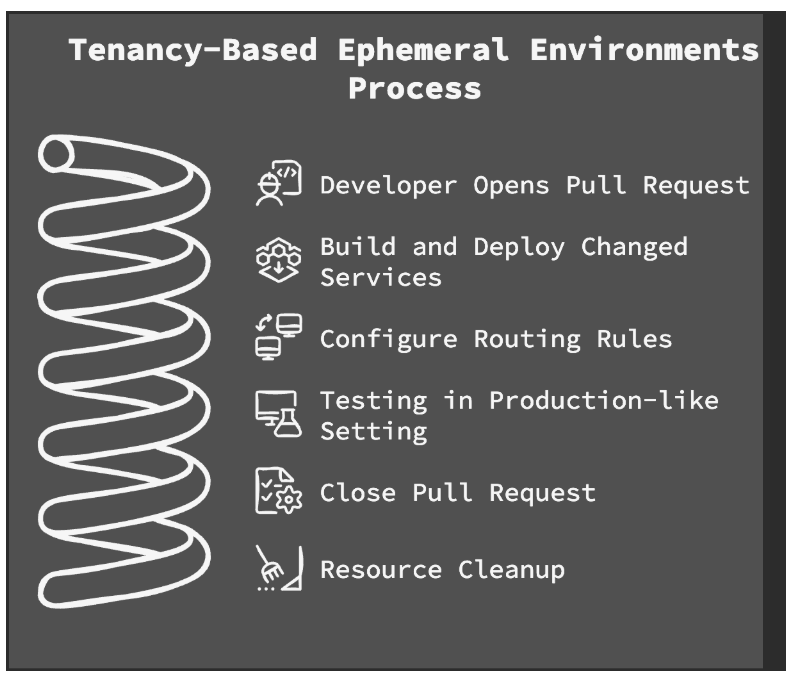
So, how does it work? Imagine every pull request spinning up an environment on demand. With tenancy, environments share the same Kubernetes cluster while isolating resources, routing and data using request-level tenancy for traffic control.
For example:
- A developer opens a pull request.
- Once images are built, only the changed services are deployed into the cluster in a sandbox.
- Routing rules are configured so that requests with specific headers are directed to the new version of the service — similar to how canaries work in production.
- Developers and QA teams test these changes in a production-like setting with shared dependencies.
- Once the pull request is closed, the environment is automatically cleaned up.
Request Tenancy as a Core Component
Request-level tenancy efficiently manages traffic without requiring fully isolated infrastructure. Service meshes like Istio or Linkerd can use unique headers to route and segment requests for each environment, allowing multiple environments to coexist with minimal resource consumption while maintaining logical isolation.
A crucial aspect of request tenancy is context propagation, which allows environment-specific metadata to travel across service boundaries. By leveraging OpenTelemetry (OTel) and baggage propagation, this metadata is automatically passed from service to service. This enables consistent environment-specific behavior and seamless rerouting using service mesh rules.
Handling Data Isolation and Message Queues
Data isolation is essential in shared databases. One common method is partitioned data, isolating tests by identifiers like org or user IDs to minimize interference. For schema changes, teams can spin up temporary containerized databases to ensure full isolation. Message queue isolation can be achieved through message-level routing using headers or by dynamically creating temporary queues. These strategies support parallel testing without disrupting shared resources.
Conclusion
If you’re already using Istio or Linkerd, ephemeral environments are well within your reach. By embracing tenancy-based environments, you’ll unlock faster development cycles, safer deployments and happier developers. For a deeper dive into the technical details, check out “Sandboxes in Kubernetes using OpenTelemetry.”
Tools like Signadot go beyond automation, offering features like local workstation-based environments, seamless support for databases and message queues, and environments that span multiple pull requests within a single routing context. They provide analytics for deeper insights and help platform teams adopt and manage these environments with ease. With support for both local and pull-request–based workflows, automated testing becomes straightforward, making rollout simpler and empowering teams to scale ephemeral environments efficiently.
So, why wait? Start exploring how tenancy-based ephemeral environments can transform your development workflow today.
The post Using Istio or Linkerd To Unlock Ephemeral Environments appeared first on The New Stack.
Comments are closed.